Introduction to Machine Learning
Published:
This post will give a brief introduction to Machine Learning.
In the field of Computer Science, to solve simple problems like the addition of numbers, sorting of numbers, matrix multiplication, etc., engineers write programs that encode those sets of rules to solve the problem and obtain the solution. As the complexity of problems increases, it becomes challenging to encode those rules, like identifying whether a cat is present in the given image and how many apples are in the picture. Hence instead of writing the programs to solve these complex problems, we approach learning systems (Machine Learning), which are not directly programmed to solve the problem but rather develop their programs based upon the examples (data) and trial and error process (experience) to solve the problem.
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on developing algorithms and models to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. These learning systems/learning algorithms (Machine Learning) incorporate the training samples’ information into the system, producing a program/algorithm that solves the problem. It involves using statistical and computational methods to enable computers to learn from examples or experiences and improve their performance on a specific task over time.
The designed algorithm might look different from the typically handwritten program by engineers, and they work very well for new data (samples). Machine learning aims to build intelligent systems which can solve complex problems and make accurate predictions.
Machine learning algorithms can be categorized into three main types: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
Types of machine learning algorithms
1. Supervised Learning:
In Supervised Machine Learning, the algorithm is trained on labeled data. The labeled data consists of input-output pairs, and the model tries to learn the mapping between the input and output. Supervised learning aims to learn a function that can generalize to unseen data. These algorithms are used in many applications, like image classification, object detection, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Supervised learning algorithms can be further divided into regression and classification. In regression, the algorithm learns to predict a continuous output variable, such as the price of pizza or the average rainfall in a given city. In classification, the algorithm learns to predict a discrete output variable, such as whether a loan can be given to an individual.
2. Unsupervised Learning:
In Unsupervised Machine Learning, the algorithm is trained on unlabelled data. Unsupervised learning aims to find hidden structures or relationships in the data.Unsupervised learning is used in many applications like clustering and dimensionality reduction. In clustering, the algorithm groups similar data points together based on their similarity. In dimensionality reduction, the algorithm reduces the number of features in a dataset while preserving the most critical information.
3. Reinforcement Learning:
In Reinforcement learning, the algorithm is trained to make decisions based on a reward system. The agent learns by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback through rewards or penalties. Reinforcement learning is used in many applications, including finance, robotics, gaming, and autonomous driving.RL algorithms train agents to buy or sell stocks based on market trends. In robotics, the agent learns to perform tasks like picking up or balancing an object. In gaming, RL trains agents to play games such as chess, Go, and poker so that agents learn to make decisions that maximize their score or win rate. In autonomous driving, the agent learns to navigate a car safely and efficiently.
Reinforcement learning algorithms can be further divided into model-based and model-free categories. In model-based reinforcement learning, the agent learns a model of the environment and uses it to make decisions. In model-free reinforcement learning, the agent learns directly from interacting with the environment.
Building any Machine Learning model/hypothesis involves two main phases: training and testing.
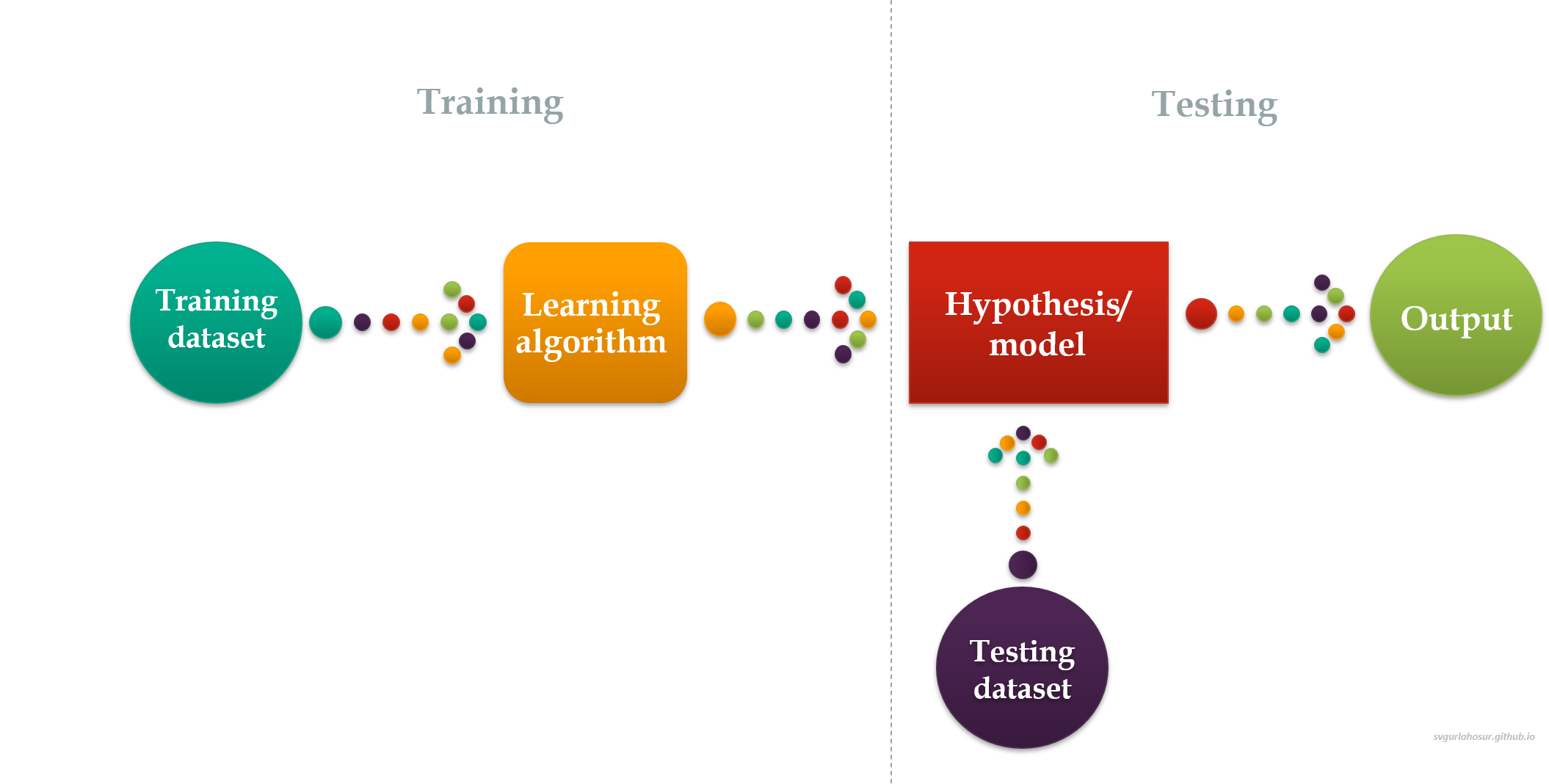
In the training phase, the machine learning algorithm builds a model using the training data to make predictions or classifications depending on the type of algorithms built. It involves steps like data preprocessing, model training, and hyperparameter tuning to optimize the model’s parameters for accurate predictions. The model is evaluated using various metrics, such as accuracy, MSE, precision, recall, and F1-score, depending on the ML algorithm.
In the testing phase, we evaluate the model performance and its generalization capabilities using the testing dataset, which is not exposed to the model during the training phase. Evaluation metrics used during the training phase will be used here also, and the model’s performance will be compared with training performance and expectations. If the model aligns with our expectations, it can be deployed in solving real-world applications. We may have to revise your hypothesis or consider retraining the model by hyperparameter tuning.

Leave a Comment